It is not hard to say that electric cars (also known as electric vehicles, or EVs) have reached a monumental turning point in this day and age. In December 2021, the sales of EVs in Europe finally exceeded the sales of diesel cars for the first time. Globally, sales of EVs reached an all-time high of 6.5 million, almost tripling the number sold in 2019. EVs are more popular than ever due to their lower emissions and maintenance cost compared to non-electric cars. With transportation being a major polluter, governments around the world have widely embraced electric cars to combat climate change. While Europe and China lead in EV sales, EVs are also becoming more widely used in the United States. In this article, we’ll explore what electric cars are and how they work.
What are Electric Cars?
Electric cars are cars that run partially or entirely on electricity, instead of only on gasoline or diesel. Additionally, they don’t usually have the typical internal combustion engine used by typical cars. This means that electric cars are not propelled forward by mixing and compressing fuel (i.e., gasoline or diesel) and air. Electric cars, instead, have a battery that supplies electricity to an electric motor to move the car forward. As a result, they generally produce less emission than typical non-electric cars. Electric cars generally fall into three different categories:
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV): BEVs are the typical cars when people talk about electric vehicles. These are vehicles that run entirely on electricity. Plugging BEVs to a charging station recharges the car’s battery.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV): PHEVs are cars with an electric motor and an internal combustion engine. They typically run-on electricity until the battery is used up. When this happens, PHEVs will use gasoline or diesel. Similar to BEVs, plugging PHEVs to a charging station recharges the car’s battery.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV): HEVs are cars that have an electric motor and an internal combustion engine. Similar to other electric cars, HEVs have a rechargeable battery. However, instead of plugging the car to a charging station, a process called regenerative braking is used to charge HEVs. Regenerative braking converts some of the energy generated from stopping the car to charge the car’s battery.
Although there are different types of electric cars, they all have the same general design and, generally, work in the same way.
Main Components of Electric Cars:
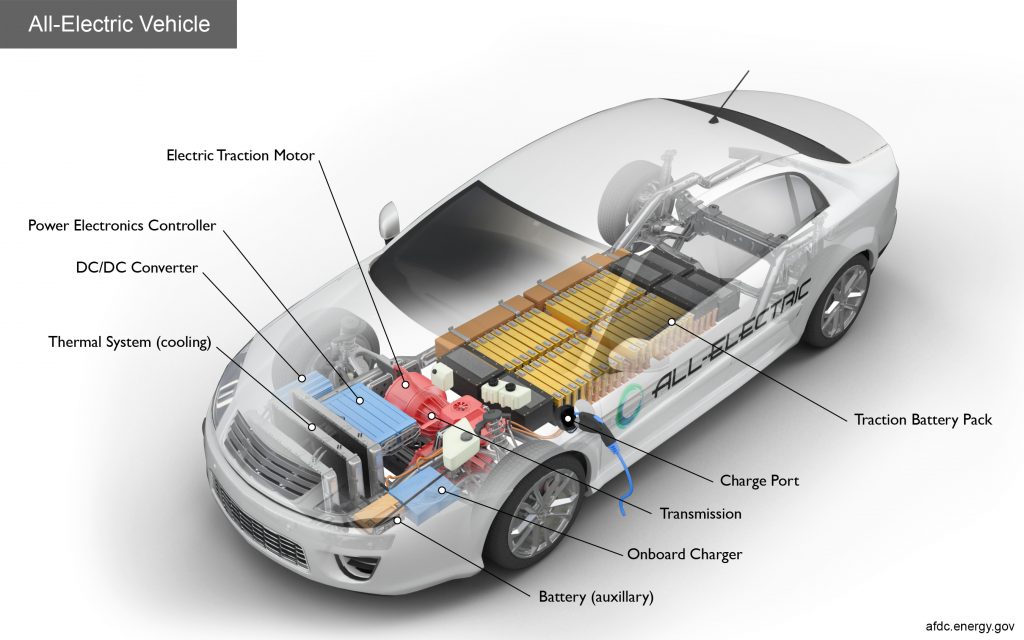
Electric cars, much like any other car, contain many different parts. However, the most important components of an electric car are the following:
- Battery: The battery supplies the necessary electricity for the electric motor to work. Typically, the battery produces electricity that passes through the controller, and then to the electric motor. The battery is usually charged by plugging in the car to a charging station.
- Controller: The controllers change the type of electric current produced by the battery for the electric motor to move the car’s wheels. Additionally, they play an important role in the electric car’s speed by controlling the amount of electricity that goes to the electric motor.
- Electric Motor: The electric motor uses the converted electricity from the controller to move the car’s wheels. The more electricity the electric motor receives from the controller and battery, the faster the electric car’s speed. Since electric motors don’t use gasoline or diesel, they don’t produce any pollution at all.
Without any of these main components, an electric car would not simply work at all.
The Science of Electric Cars:
To explain how electric cars work, we need to understand what electricity is first. Electricity, put simply, is a form of energy produced when charged particles, usually electrons, move. The movement of these charged particles is called an electric current. Electric current occurs because a force called voltage is produced which “pushes” the charged particles around a circuit. Voltage “pushes” electrons from negatively charged areas (i.e., areas with more electrons) to more positively charged areas (i.e., areas with fewer electrons). A simple and general way to understand electricity is to imagine electricity as water in a faucet. Each water droplet is a charged particle, the water flowing is electric current, and water pressure is voltage. Much like electric current, water in a faucet only flows in a specific direction. Now that we understand how electricity works, we can now explain how an electric car works.
The battery is the heart of an electric car. Without the battery, an electric car will not work. Often, when we think of batteries, we usually think that they store energy. This is partially correct. A better understanding would be that batteries convert chemical energy to electrical energy through various chemical reactions called redox reactions. These reactions are crucial in understanding how electric cars work.
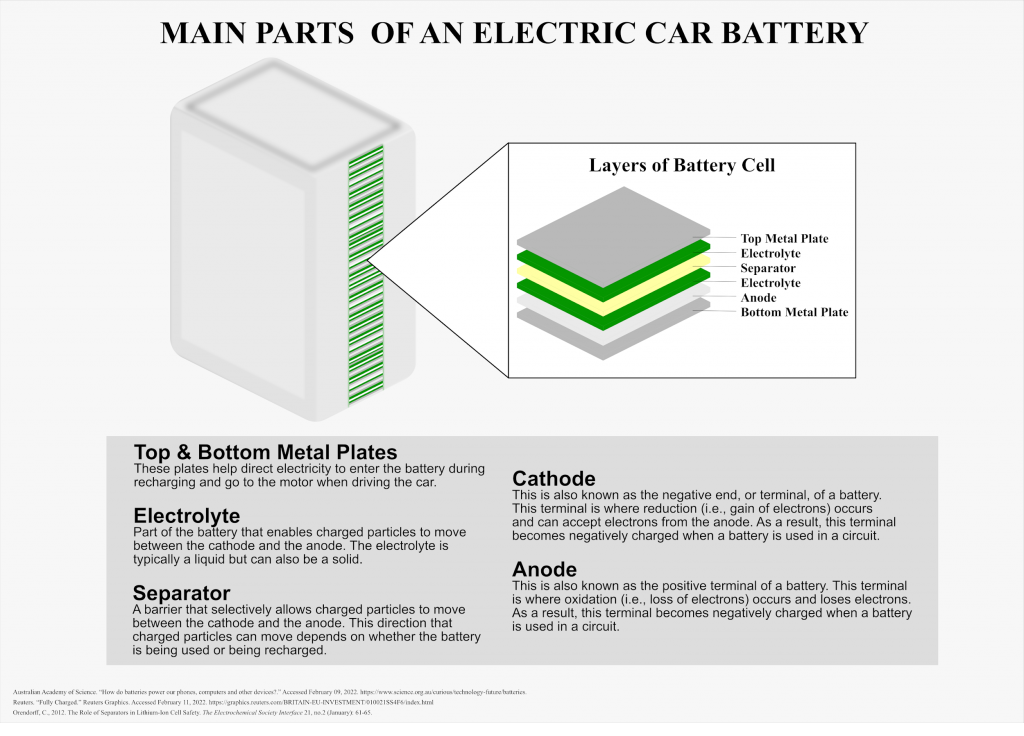
Redox reactions, or reduction-oxidation reactions, are the reactions responsible for creating the electricity for electric cars to work. Reduction is the gain of electrons while oxidation is the loss of electrons. At the anode of the battery, oxidation occurs and the anode loses electrons. This makes the anode end of the battery positively charged. Simultaneously, at the cathode of the battery, reduction occurs and this end can accept the electrons from the anode. This makes the cathode negatively charged. As a result, these reactions create a charge difference which allows electric current to flow through the circuit. Due to the separator, electrons from the anode cannot simply pass through the electrolyte to reach the cathode. Instead, electrons from the anode must pass through the entire circuit to reach the cathode. The resulting flow of electrons creates the electric current that the electric can use to propel the car forward.
Receiving electricity from the battery, the electric motor turns on and converts the electrical energy to mechanical energy. Consequently, the activated electric motor allows the wheels to move, enabling the car to move forward.
How do electric cars benefit the world?

There are many reasons why electric cars becoming more popular benefits everyone. Electric cars, compared to non-electric cars, are generally more fuel efficient and produce less noise overall. However, the biggest benefit of electric cars is that they produce less pollution compared to non-electric cars. While some sources online report that electric cars do not produce any pollution, this is not completely true. Electric cars that run entirely on electricity produce no emissions from their tailpipes. However, creating the electricity to charge electric cars and making their batteries are processes that usually rely on fossil fuels. These processes make manufacturing electric cars produce more pollution than manufacturing non-electric cars. Nevertheless, due to their better fuel efficiency, electric cars still produce less pollution in their lifetime than non-electric cars.
With transportation being a major source of pollution, it is without a doubt that electric cars will help slow down climate change. However, it is important to remember that using electric cars alone is not a full proof solution. Using more renewable energy, planting more trees, eliminating fossil fuels, and many other actions are needed to prevent climate change. This will require major changes in the way we live our lives and how the world works. Nevertheless, using electric cars is certainly a significant first step to making the world a more clean and sustainable place.